ROOM
68
Astronautics
Analysis (CRIOP) method. It was validated in
a case study on crew-ground interactions at
the European Astronaut Centre (EAC) and
at the Control Centre of International Space
Station Columbus module (COL-CC).
• Human Automation Interaction (HAI, 2014)
focused on the development of quantitative
formal modelling and verification
approaches for the design of automated
systems in view of human error. Case
studies were conducted on Columbus
Environmental Control and Life Support
System (ECLSS) operations from COL-
CC, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle operations,
and Control Centre of European Tracking
Stations (ECC) operations.
• Integrated Failure Analysis (IFA, 2015)
aimed to provide a qualitative and
quantitative method to model success
and failure in complex socio-technical
systems with a focus on space systems
design and operations, including the
organisational dimension.
• Several applied design studies addressed
aspects as diverse as console design and
audio alarms in control rooms.
A two-year research project at the European
Space Operation Centre (ESOC) on the ‘Human
Element and System Resilience’, completed in
2015, focused on ESA’s operations centre and
the contribution of flight control teams to
overall system safety. Aside from introducing the
concept of ‘resilience’ and ‘resilience engineering’
to stakeholders in quality, special projects and
training, this study identified work patterns in
special and routine operations based on more
than 300 hours of direct field observations in
the operations centre, and proposed practical
and policy-related recommendations based on a
review of smart practice in external high-reliability
organisations in seven safety-critical sectors
outside the space domain.
The HUDEP community also brought together
over a dozen experts to complete the revision of
the Human Dependability Handbook ECSS-Q-HB-
30-A with a focus on Human Error Analysis.
Current initiatives
The external and internal efforts conducted as
part of the Human Dependability Initiative at
ESA captured the emerging consensus of space
agencies to systematically include Human Factors
considerations in the design and operation of
crewed and robotic missions.
Recent external contracts commissioned by
ESA predominantly focused on raising awareness
and developing methods to address human
dependability, some with applied case studies:
• The Human Dependability Model (HuDeM,
2013) was a qualitative study to develop and
validate a human dependability model and
analysis approaches. The project primarily
focused on control centre activities and
looked in depth at one particular approach,
the Crisis Intervention and Operability
Humans should always be
at the centre of any future
advanced systems designed for
space exploration
Below: ESA astronaut
Samantha Cristoforetti
working on the TripleLux
experiment, an
investigation into the
effects of microgravity on
immune cells. A smoke
detector deep in the belly
of the Biolab rack on
Columbus had to be
replaced quickly before
the cell cultures expired.
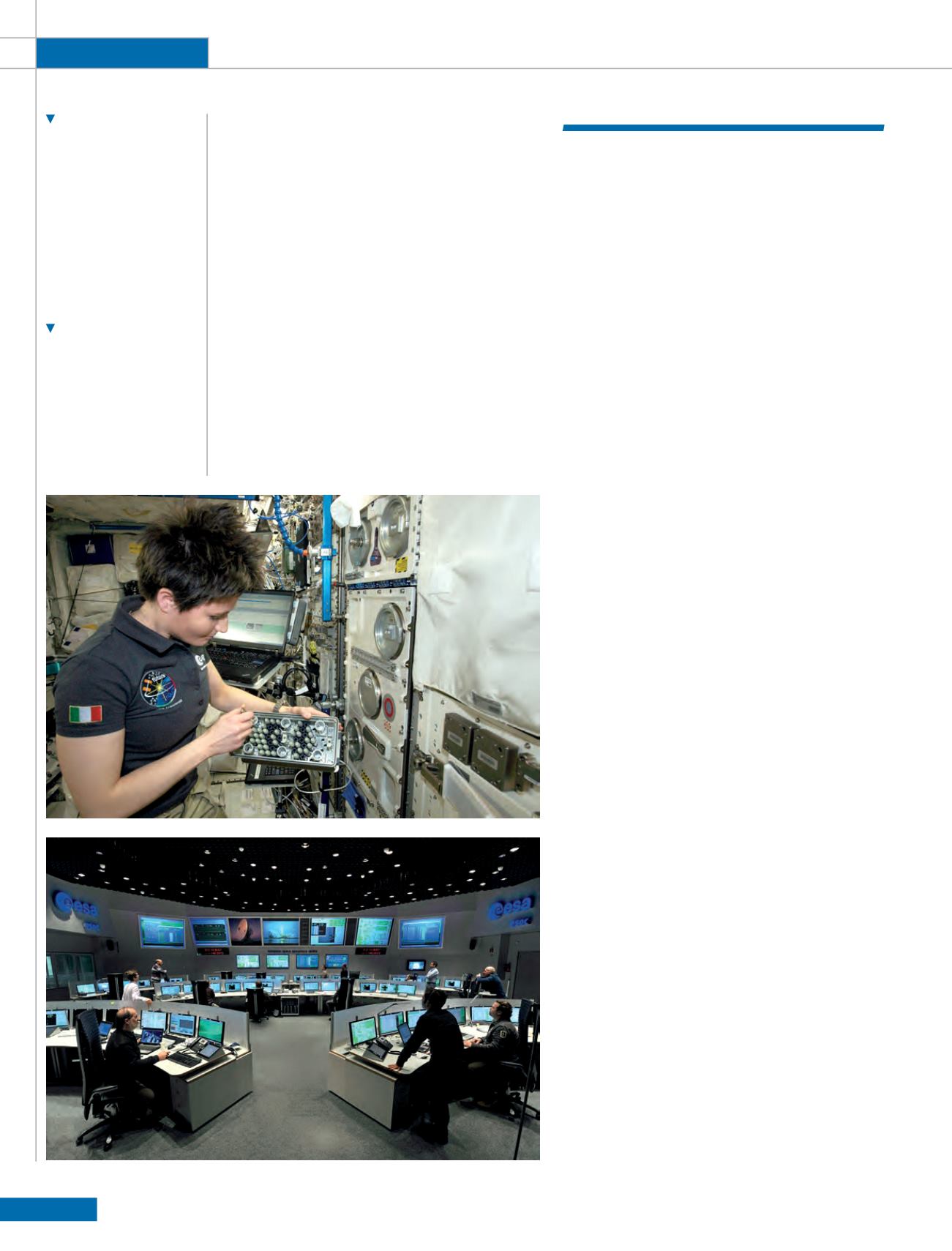
Bottom: Inside the
European Space
Operations Centre (ESOC)
engineers control
spacecraft in orbit,
manage the global
tracking station network,
and design and build the
ground systems that
support missions in space.


