ROOM
63
Astronautics
For example, the vertical integration of upstream
with downstream done by Planet gives it control
over the entire supply chain of production (agile
methods of construction of satellites) to provide the
four Vs (volume, velocity, variety and veracity) of
medium-resolution imagery.
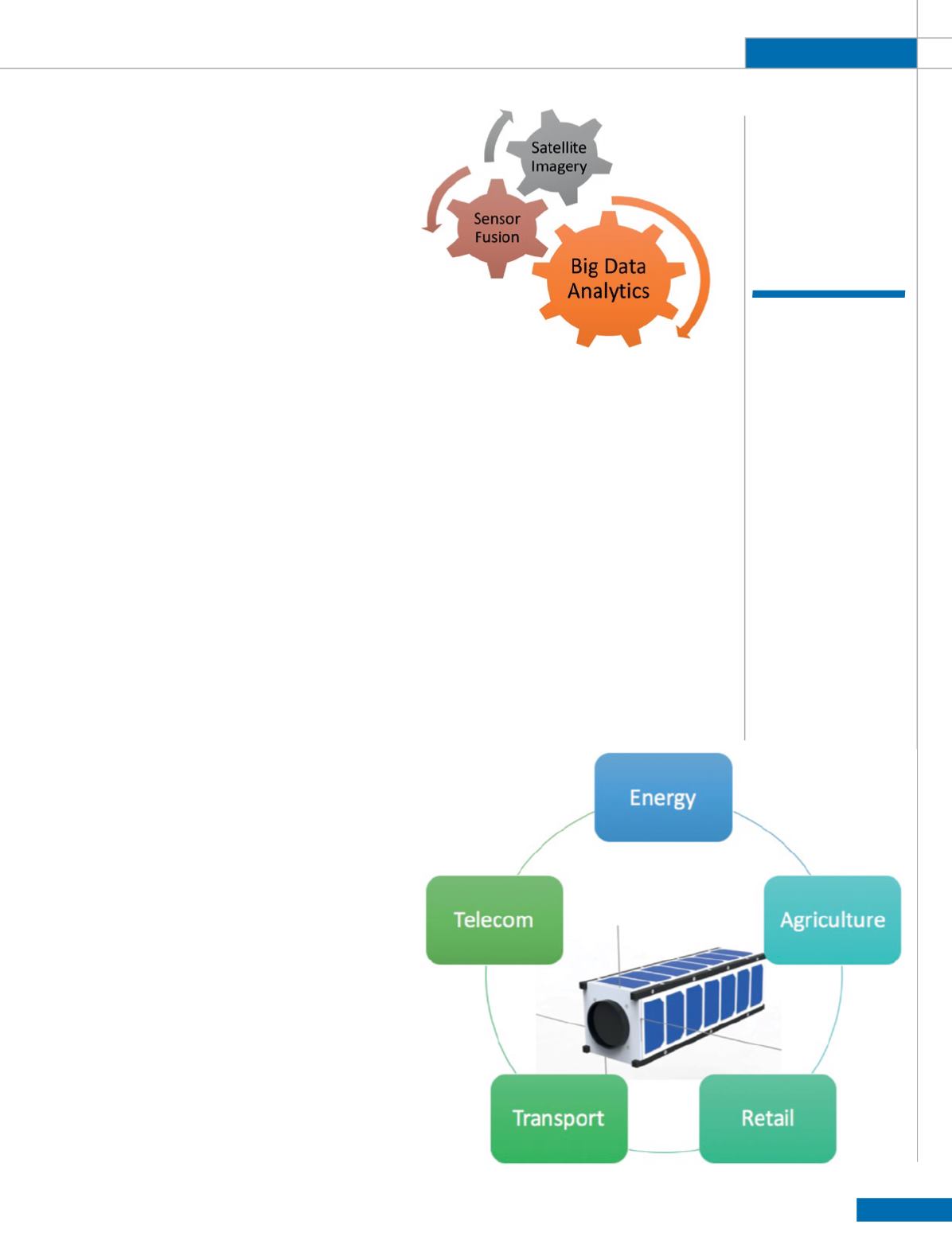
One of the strong pillars of NewSpace is the
dynamism around integrating space-based products
and services into traditional industries such as
energy, agriculture, retail, transport, internet/
connectivity, etc. NewSpace companies are planning
to pick up the buck where traditional space
companies have flattened in technology and growth.
There is, for example, a whole new ecosystem of
Earth observation (EO) downstream applications
ventures that want to go beyond traditional
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) but using
satellite data with ground based sensors in creating
data stacks that can add specific industry and
decision intelligence to an array of industries.
The low Earth orbit (LEO) constellation-based
satellite services - including Internet, IoT, AIS,
ADS-B, GPS-RO - integrate into different B2B
or B2C offerings that are primarily agnostic to
what happens in the government procurement
realm. There is no doubt that a large percentage
of NewSpace ventures will fail and ultimately the
market size of several of these services may be
limited to a few players even though many of these
services are required today and can complement
or integrate into industries on the ground.
A step beyond
The proof of availability of several reliable and
scalable (hardware/software) platforms, trends
towards low-cost access to space, integration into
industry 4.0, and global business models are some of
the key reasons for new actors to consider investing.
Initially fuelled by private investors, NewSpace
has arguably alerted states to opportunities
which, in turn, is leading to some states actively
pursuing investments and creating regulatory
frameworks to promote, for example, space
resource utilisation.
The latest prime movers on this front are
states such as Luxembourg and the United Arab
Emirates which intend to offer an attractive
overall framework for space resource utilisation
related activities, including but not limited
to the legal regime. These governments are
pushing dedicated research and development
(R&D) funding into technologies related to space
resource utilisation, in line with the ambition to
become if not international, then regional hubs for
the exploration and use of space resources.
NewSpace India
India’s space programme dates back to the early
1960s and today stands in the midst of major
achievements including having homegrown reliable
rockets and satellites providing applications serving
the needs of society. However, the entire value chain
from upstream to downstream is mostly occupied
by the government ministries/organisations. There
are no independent verticals (EO, navigation,
communication) in which there is an upstream to
downstream connection that is entirely private
sector driven.
Due to the sheer increase in the space-based
services required in the country that has expanded its
footprint in EO, navigation and telecommunications,
the private sector is now being engaged in creating an
Assembly, Integration and Testing (AIT) consortiumof
industries to produce navigation satellites and a Joint
Venture (JV) for producing the Polar Satellite Launch
Vehicle (PSLV). These strategies are possibly the next
India’s entire
value chain
from upstream
to downstream
is mostly
occupied by the
government
ministries/
organisations


